
Chiropractor Chandler AZ
Pronator Teres Trigger Point
The pronator teres has two heads with separate origins: the humeral head - medial supracondylar ridge of humerus (common flexor tendon), and the ulnar head: coronoid process of ulna. Its insertion is in the middle of the lateral surface of the body of the radius. The nerve that serves the pronator teres is the median nerve.
The trigger point of the pronator teres is located at the inside of the elbow (medial elbow), and the path of referral pain extends from the trigger point down the forearm to the wrist, hand and thumb. Secondary symptoms can include volar (volar means “located on the same side as the palm of the hand”) finger pain, volar wrist pain and palmar pain. The images below show the path of the referral pain caused by the pronator teres trigger point, with a darker red area that shows where the pain is usually pronounced.
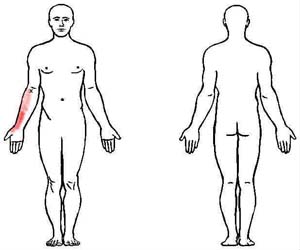
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the first thought people have when they feel pain radiating from the elbow toward the thumb. Carpal tunnel syndrome is compression of the median nerve anywhere along its path from the neck through the elbow and into the hand. Compression of the median nerve produces numbness, tingling, weakness, and loss of sensation in the thumb, index, and middle fingers.
The median nerve runs underneath the pronator teres muscle at the elbow. Overworking the pronator teres muscle can lead to spasms which can compress the median nerve and cause carpal tunnel syndrome from the pronator teres. However some people who are diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome actually have trigger points of the pronator teres muscle radiating from the elbow to the hand. Especially when the NCV or nerve conduction velocity test does not show a loss of median nerve function.
Weakness and pain in the thumb is not truly diagnostic of any one condition. Multiple muscles radiate pain into the thumb. Reproducing the trigger point is always required for a proper diagnosis. Palpation of the pronator teres muscle should produce the classic pain radiating from the elbow towards the thumb, and decrease in pressure on the muscle will reduce the pain.
Conservative Treatments
Therapeutic treatments for addressing soft tissue injuries involve massage therapy, manual therapy, trigger point therapy, Graston Technique, or Active Release Technique. These treatments increase blood flow, decrease muscle spasms, enhance flexibility, speed healing, and promote proper tissue repair.
When these treatments are incorporated into a treatment plan patients heal faster and are less likely to have long-term pain or soft tissue fibrosis or scar tissue in the injured muscle. These soft tissue treatments are incorporated with therapeutic exercise and flexibility programs.
Treatment for shoulder injuries often requires a variety of exercises, stretches, conservative treatments, medical treatments, and home therapies. Shoulder injuries can become chronic if the appropriate steps are not taken.
Elbow injuries often occur in people with severe or chronic shoulder injuries. People begin trying to alter their shoulder motions to protect it. Unfortunately these altered body mechanics tend to overwhelm the muscles and tendons around the elbow. People often develop a secondary cubital tunnel syndrome, lateral epicondylitis, tricep tendonitis, medial epicondylitis, pronator teres syndrome, double crush, carpal sprains, wrist tendinitis, de quervain's tendonitis, finger extensor strains, or carpal tunnel syndrome.
Treatment for elbow injuries can be extensive if the tendinosis is severe. Mild strains can be treated at home with PRICE, home stretches, and exercises. Don’t wait for damage to both the shoulder and elbow to seek treatment and therapy.
Medical Treatments
NSAIDs are often prescribed for the initial acute injury stages. In severe cases that involve multiple joint regions, muscle relaxers or oral steroids can be given. Trigger point injections, botox, or steroid injections can be treatment options. Pain management is not usually required unless stronger medications or joint injections are required for treatment.
MRI and X-rays will not usually be ordered to evaluate mild to moderate muscle, tendon, and ligament injuries. Severe cases may utilize advanced imaging to rule out bone fractures, edema, nerve entrapments, tendon or muscle ruptures. NCV testing may be utilized in cases that also involve muscle, sensory, or reflex loss.
Cervical spinal disc bulges and herniations onto the spinal cord or nerve root produce different symptoms and location of symptoms. Pain radiating in the hand is one symptom; along with numbness, weakness, fatigue, loss of sensation, or reduced reflexes. Your chiropractor, physical therapist, occupational therapist, or physician will evaluate your condition and make a proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations. Ask them any questions you might have about your injury.
Many people do have arthritis or degenerative changes in their elbow, wrist, finger, or thumb joints. Arthritis does not mean you will always have pain in the joints. Degenerative arthritis means the structural Integrity of the bones have changed which alters its gliding, sliding, and hinging motions. The more severe the arthritic changes the easier it becomes to aggravate the joint and produce pain.
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis will also slow healing and recovery time. People with severe arthritis can have no pain in a joint. In fact many times people blame their arthritis pain on tendinosis or tendonitis of the tendons that attach around the joint. Conservative treatment can improve hand and wrist pain; and people will have dramatically less pain in joints that have arthritic changes.
Conclusion
The upper extremity works as a comprehensive unit performing many of the repetitive tasks at home, work, and recreational sports. Injuries to one area of the musculature often indicate that additional damage has been incurred by other muscles.
Many therapeutic exercises can help restore proper strength and endurance to the elbow flexor muscles. Isometric exercises are often the initial treatment exercises. Followed by single plane rubber band exercises for elbow flexion, extension, pronation, and supination movements. Dynamic exercises involving stability ball push-ups can be performed on the wall or floor. The more unstable of the surface the more effort and stabilization is required of all the upper extremity muscles.
Push-ups on a stability ball enhances neuromuscular learning throughout the neck, scapula, shoulder, upper arm, and lower arm muscles. Additional strength exercises can be found on the arm and shoulder strengthening pages.
Our Chandler Chiropractic and Physical Therapy clinic treats patients with a variety of muscle, tendon, joint, and ligament injuries. The clinic provides treatment for runners, tri-athletes, and weekend warriors in addition to common headache, neck, and back patients traditionally seen in Chiropractic, Physical Therapy, Massage Therapy clinics. We work with all ages and abilities of the residents in Phoenix, Tempe, Gilbert, Mesa, and Chandler AZ.